The impact of AI on the labor market is becoming increasingly evident as researchers delve into long-term trends linked to technological advancements. Recent studies have uncovered a significant shift in job dynamics, suggesting that AI is not just displacing jobs but also reshaping the entire job market landscape. As we navigate through this era of rapid technological integration, terms like “technology in workforce” and “job market changes” are more relevant than ever. Economists have observed a phenomenon known as “occupational churn,” which highlights the constant fluctuation of roles within the economy due to AI innovations. This evolving narrative raises critical questions about the future of work and how we can adapt to potential challenges like AI job displacement while harnessing its benefits for the workforce.
The influence of artificial intelligence on employment trends is sparking widespread discussion about the future of occupational roles. With terms like automation revolution and career transformation permeating conversations, it’s crucial to understand the deeper implications of these changes. As new technologies reshape the job landscape, we are witnessing a unique blend of opportunities and challenges that characterize the current employment climate. The discussion not only revolves around technology’s role in the workforce but also highlights the ongoing job market transitions that many sectors are facing. Understanding this shift is essential for both workers and employers aiming to thrive in a rapidly changing environment.
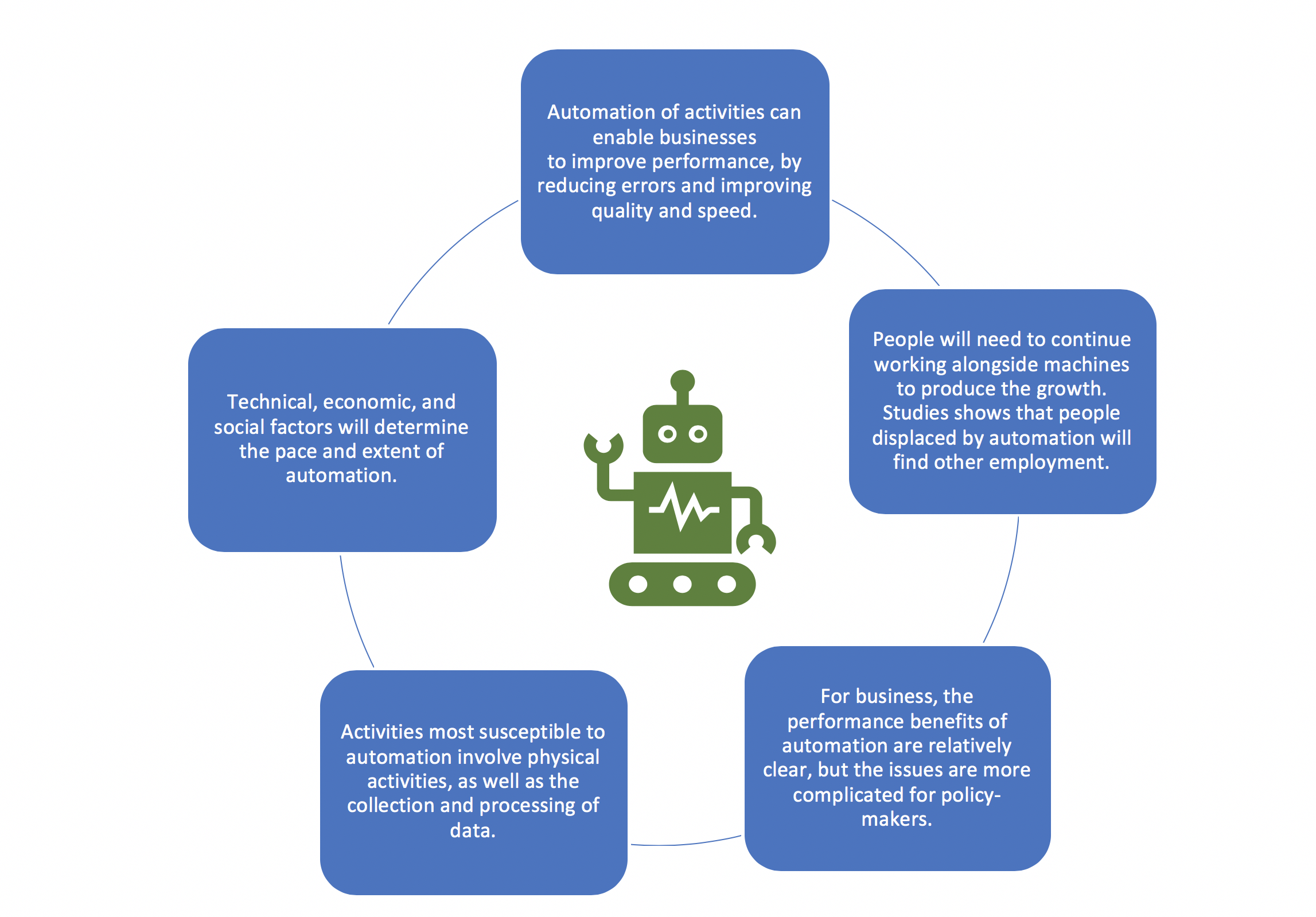
Understanding AI’s Role in Labor Market Transformation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) plays a pivotal role in reshaping the labor market, introducing profound changes to job structures and workplace dynamics. A recent study underscores how AI advancements have initiated a wave of ‘occupational churn,’ shifting traditional employment landscapes remarkably. As AI tools become mainstream, they enhance efficiency but also pose challenges of job displacement for roles that can be automated. This transformation is reminiscent of past technological revolutions, highlighting the urgent need for adaptation in labor strategies, workforce skill development, and educational initiatives.
The implications of AI on the job market are already visible; industries are increasingly relying on advanced technologies to streamline operations, leading to a rising demand for skilled labor in tech-related fields. Professions in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) are experiencing considerable growth, a trend that reflects the labor market’s evolving demands. This necessitates a reevaluation of job creation strategies, as traditional roles risk extinction in the face of rapidly accelerating automation fueled by AI.
Job Market Changes Driven By AI
Research indicates that the U.S. job market has entered a pivotal phase due to the rise of AI, pushing economists to rethink historical patterns. The relatively stable period between 1990 and 2017 has now given way to increased volatility, driven by gradual technological adoption and modernization. Job polarization, previously dominant in discussions about labor trends, is being replaced by a new phenomenon as firms increasingly prioritize high-skilled roles, leaving behind lower-paid positions, thus altering the wage distribution significantly.
Despite prior fears of an unemployment crisis due to AI and automation, the latest findings reveal an alarming downturn in specific sectors. Retail sales jobs, for instance, have witnessed a stark decline attributed not only to consumer habits shifting towards e-commerce but also to heightened investments in AI technologies that optimize operational functionalities. This dual impact redefines work opportunities, underscoring the collaboration necessary between technology and human labor in future job market configurations.
The Effect of Occupational Churn on Employment Strategies
Occupational churn within the labor market illustrates the ongoing reorganization of work driven by technological advancements, particularly AI. This phenomenon highlights the need for progressive employment strategies that can cater to the ever-changing demands of the economy. As companies adapt to leveraging AI for operational efficiency, the nature of jobs is evolving, thereby necessitating a skilled workforce equipped with advanced technical capabilities. Economists argue that understanding this churn can provide insight into how to prepare future workers for a landscape increasingly dominated by technology.
For companies seeking growth, it is essential to develop employment frameworks that integrate continuous training and upskilling for workers. The transformation induced by AI means that businesses will likely require different competencies and skills than in previous decades. Hence, fostering a culture of lifelong learning and flexibility within workplaces can mitigate risks associated with job displacement due to AI while also promoting innovation and productivity.
Future of Work: Embracing AI Advancements
As we look towards the future of work, the integration of AI presents both opportunities and challenges that businesses must actively engage with. The automation of routine tasks enables employees to focus on more complex responsibilities, prompting a shift in required skill sets. The expanding role of AI in industries showcases the need for workers to become more adept with technology, fostering an environment where creativity and critical thinking can flourish alongside machine capabilities.
Moreover, the future workforce must be resilient, adaptable, and well-versed in technology-driven innovation, allowing individuals to navigate the changes prompted by AI. Embracing these advancements requires collaborative efforts between educational institutions and employers, ensuring that workers are prepared for an emerging landscape rich with technological potential while managing the associated risks of job displacement.
AI Job Displacement and Workforce Realignment
The potential for AI-related job displacement has elicited substantial concern among workers and policymakers. With the rise of AI in various industries, low-skilled jobs in sectors like retail and service paces are rapidly diminishing, highlighting a critical need for workforce realignment strategies. In contrast, there is a corresponding increase in the demand for skilled professionals in fields such as software development and data analysis, indicating a significant shift in job availability. This necessitates immediate action to prepare the existing workforce for new challenges and opportunities.
To address these shifts, labor market stakeholders must collaborate on policies that support retraining and upskilling programs for displaced workers. Investing in vocational training and educational programs that align with emerging job opportunities is vital to ensuring a sustainable workforce. Furthermore, a focus on creating an inclusive workforce where all demographics are supported in their transitions can foster greater economic stability amid these technological changes.
Navigating Automation Anxiety in the Workforce
Automation anxiety is a prevalent sentiment among workers as AI continues to reshape job responsibilities and workforce structures. Many fear the working landscape’s rapid evolution could render their skills obsolete, prompting organizations to find ways to communicate the benefits of AI as a complement to human labor rather than a replacement. Addressing these concerns proactively can help mitigate fears and promote a more collaborative approach to technology in the workplace.
Encouraging a positive narrative around AI integration—where automation augments rather than eliminates human roles—will be essential to alleviating workforce anxiety. Companies can foster a culture of innovation and acceptance by investing in communication and training strategies that focus on AI’s empowering capabilities, preparing employees to thrive alongside automation. This approach not only creates a more engaged workforce but also capitalizes on the synergies between human intelligence and machine efficiency.
Challenges and Opportunities in AI-Driven Employment
The rise of AI brings forth both challenges and opportunities that will define the future of employment. While certain sectors face declining job opportunities, others are poised for significant growth, underscoring the need for adaptability within the workforce. Companies that embrace these changes and strategically approach the integration of AI can create new avenues for employment and innovation, positioning themselves at the forefront of their industries.
However, organizations must also be cognizant of potential pitfalls, such as the risk of widening the skills gap and creating disparities in access to new job opportunities. Proactive strategies should be developed to ensure that all workers are prepared for transitions rather than left behind in the wake of AI changes. This can include partnerships with educational organizations to create accessible, relevant training programs that fast-track individuals into evolving job markets.
Revolutionizing Education to Adapt to the New Job Market
To keep pace with the shifting demands of the labor market driven by AI, education systems must evolve significantly. Integrating technology into learning processes and focusing on STEM disciplines will be crucial in preparing students for future careers. By incorporating hands-on experience and real-world applications into curricula, educational institutions can better equip students with relevant skills that align with industry expectations.
Moreover, ongoing collaboration between educational institutions and businesses can create a feedback loop that ensures graduates are ready to meet the evolving challenges posed by technology. Emphasizing interdisciplinary learning, critical thinking, and adaptability will be vital in developing a workforce capable of navigating an increasingly AI-centric job landscape.
AI’s Influence on Labor Politics and Economic Policies
The advent of AI carries significant implications for labor politics and economic policies. As job displacement becomes a reality, there will be growing pressure on policymakers to implement frameworks that protect workers while fostering innovation. This shift may lead to enhanced labor rights, a reassessment of minimum wage policies, and the introduction of universal basic income discussions to safeguard those displaced by technology.
The intersection of AI and economic policy will require careful consideration, balancing the need for technological advancement with ethical labor practices. Policymakers must engage in dialogues with various stakeholders, including businesses, labor unions, and educational institutions, to develop strategies that promote inclusive growth in an ever-evolving job market influenced by AI.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is AI impacting the labor market today?
AI is currently reshaping the labor market by driving significant changes in job demand, particularly in high-skill sectors. As the study by economists David Deming and Lawrence H. Summers indicates, AI is leading to the creation of more jobs in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM), while also contributing to declines in low-paid service jobs. This impact exemplifies how AI influences occupational churn in the workforce.
What trends are emerging due to AI’s impact on the job market?
The emerging trends due to AI’s impact on the job market include a shift toward well-compensated roles requiring advanced skills, a significant rise in STEM jobs, and a decline in low-wage service employment. These trends highlight how the introduction of AI technologies is changing the distribution of jobs and creating volatility within the labor market.
Is AI causing job displacement in the workforce?
Yes, AI is contributing to job displacement in certain sectors of the workforce, particularly in retail and low-paid service jobs. The research shows a notable drop in retail sales positions, driven in part by the adoption of predictive AI technologies in e-commerce. While AI creates opportunities in high-skill jobs, it also poses long-term threats to roles that are more susceptible to automation.
What is occupational churn, and how does it relate to AI’s impact on labor?
Occupational churn refers to the natural turnover of jobs within the labor market, including the rise and fall of various professions. The study by Deming and Summers reveals that technological disruptions, including advancements in AI, significantly influence occupational churn. AI is currently accelerating changes in job distributions, leading to increased volatility and shifts in employment trends.
What does the future of work look like with AI in the job market?
The future of work with AI in the job market suggests increased demand for skilled labor, particularly in STEM fields, while potentially diminishing opportunities in routine, low-wage positions. As AI technology becomes more integrated into various industries, workers may need to adapt to new roles, enhancing their skills to remain competitive. This transformation emphasizes a need for continual education and training to navigate the evolving job landscape.
How can workers prepare for the job market changes due to AI?
Workers can prepare for job market changes due to AI by investing in skills development, particularly in areas like technology and data analysis. Focusing on acquiring competencies that AI is less likely to automate—such as problem-solving, creativity, and interpersonal skills—can also help professionals remain valuable in the evolving labor market influenced by AI.
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Occupational Churn | Historical measurement of job stability and volatility, revealing periods of consistency followed by recent shifts. |
| Job Polarization | A shift towards high-paying jobs requiring advanced skills has replaced the earlier trend of low-paid job growth. |
| STEM Job Growth | Significant increase in STEM employment, growing from 6.5% to nearly 10% of jobs, indicating a rising investment in technology. |
| Decline in Low-Paid Service Work | Flat or decreasing job levels in low-paid service sectors, with suggestions that many of these roles may not return post-pandemic. |
| Retail Decrease | A sharp drop in retail jobs due to e-commerce adoption and shifts towards AI-enhanced shopping experiences. |
Summary
The AI impact on the labor market is already evident as it reshapes job dynamics across various sectors. New research indicates that while there was previously a period of stability, recent trends highlight significant disruptions caused by AI. From an increase in high-skilled job opportunities to a concerning decline in traditional retail and low-paid service roles, the effects of AI are multifaceted. Economists suggest that these changes will continue to evolve, implying that understanding AI’s influence is crucial for workers in all industries. Ultimately, professionals must adapt to remain competitive in a landscape increasingly defined by technological advancement.