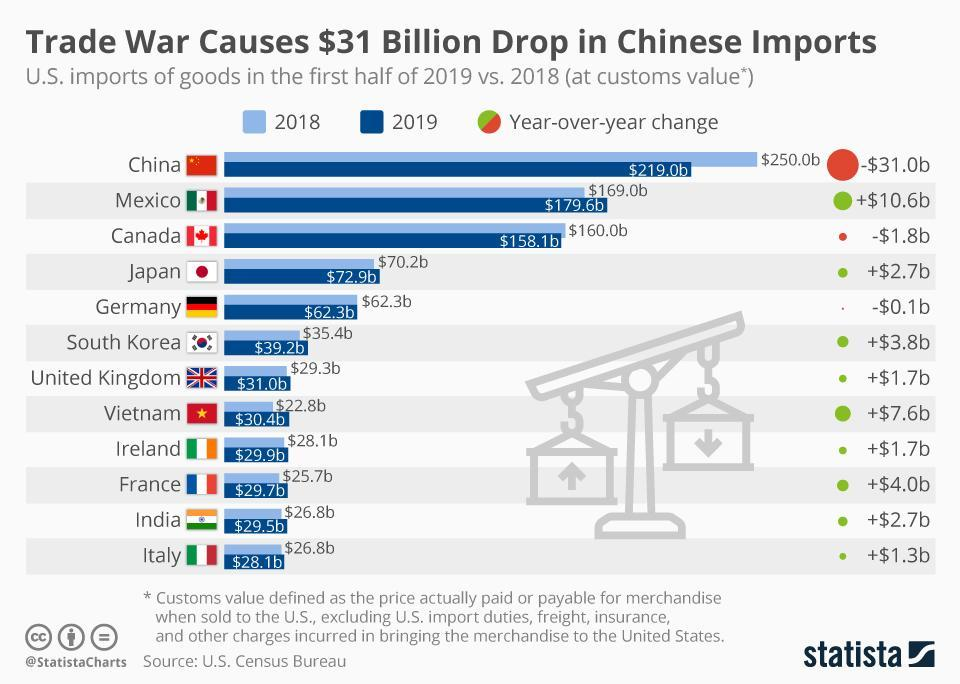
The impact of tariffs on the U.S. economy, particularly those targeting China, has become a hotly debated topic in recent economic discussions. As tensions rise in U.S.-China trade relations, the introduction of stiff tariffs could lead to significant repercussions not only for China but also for American consumers. Economists warn that these tariff implications for consumers may manifest in higher prices and increased uncertainty in the global supply chain. Additionally, such trade barriers could potentially weaken the U.S.’s ties to traditional allies and create opportunities for China to solidify its economic relationships elsewhere. As stakeholders navigate this intricate web of trade dynamics, understanding the broader implications of these tariffs is crucial for anticipating future market conditions and economic strategies.
The repercussions of imposing tariffs on imported goods from China are reverberating throughout the global economy. These protective measures, designed to revive domestic industries, may inadvertently escalate costs for American households and disrupt established supply chains. While the strategy aims to strengthen U.S. economic positions, it also risks alienating key international partnerships. The shifts in trade could prompt China to explore alternative alliances, impacting the geopolitical landscape. As we analyze these developments, it becomes clear that the ramifications stretch far beyond national borders and economic sectors.
The Rising Stakes in U.S.-China Trade Relations
The evolving U.S.-China trade relationship poses significant implications for both nations, driven largely by emerging tariff policies. As political leaders contemplate imposing hefty tariffs, many are concerned about the repercussions on domestic economies. While the goal may be to bolster American industry, the impact of tariffs on the U.S. economy could ripple through global supply chains, causing price increases for consumers and altering market dynamics significantly. Economists argue that these tariffs could stymie economic growth at home, triggering inflation and supply shortages when goods become more expensive and less available.
Moreover, the complication arises from the intertwined nature of global trade where countries heavily rely on each other’s goods and services. The effects of increased tariffs can lead to higher operating costs for American businesses reliant on affordable imports from China, ultimately passed down to consumers. In this scenario, businesses may face stark choices: they can either absorb the increased costs and risk reduced profit margins or pass them on to customers, which could lead to a significant spike in prices. The long-term consequences could foster a rift in U.S.-China relations, complicating not only bilateral trade but broader diplomatic ties.
Impact of Tariffs on American Consumers
The implications of increased tariffs directly affect American consumers, who may find themselves at the mercy of rising prices. Should tariffs on goods from China soar to 60% or more, everyday items like electronics, clothing, or household goods could see dramatic price hikes. The consumer market would inevitably feel the effects as manufacturers react to higher import costs, often leading to reduced purchasing power for average American households. This scenario raises concerns about inflation and economic strain on families, who might struggle to afford basic necessities amidst dwindling wages and increasing living expenses.
Additionally, the impact extends beyond just pricing; American consumers may also experience a drop in product variety. Tariffs could compel retailers to limit inventory choices or abandon certain imported goods altogether. As American companies look to mitigate financial losses, they may decide to source products from closer or more economically viable countries, potentially sacrificing quality and variety. This shift could reshape the consumer landscape in ways that complicate purchasing decisions and influence long-term brand loyalty as consumers adapt to new alternatives.
Global Supply Chain Disruptions Due to Tariffs
One of the most immediate concerns regarding the potential for increased tariffs is the possibility of global supply chain disruptions. In an era of hyper-connected economies, many products are manufactured using components sourced from various countries, including China. A sudden imposition of high tariffs complicates logistics, potentially leading to production delays and increased costs across multiple industries. Companies may find themselves scrambling to adjust their supply chains in order to remain competitive, all while trying to forecast market needs amidst rising uncertainty.
Furthermore, such disruptions can have cascading effects, threatening the stability of international markets. As firms seek alternative suppliers, they may inadvertently drain resources from smaller economies, impacting their growth as well. Unintentional repercussions of a U.S.-China trade war could create shortages and drive up prices in other markets reliant on similar supply chains, resulting in a complex web of economic impacts. These disruptions may ultimately hinder the global recovery from recent economic setbacks, reinforcing the need for careful policy deliberation that considers the interconnected nature of modern trade.
China’s Economic Strategy in Response to Tariffs
In anticipation of increasing tariffs, China has been strategizing its economic response to mitigate potential damage and reposition itself within the global market. The Chinese government acknowledges the dangers of overcrowded export markets and is keen to diversify its trade partnerships. This strategic pivot includes expanding into emerging markets across Southeast Asia and Africa, seeking new opportunities to compensate for potential declines in exports to the U.S. Tariffs could catalyze a more aggressive approach to developing relationships with other economies that are favorable toward China, turning adversity into strategic opportunity.
Moreover, China is likely to leverage its economic influence to forge new alliances that could blunt the effects of tariffs. For instance, by bolstering trade agreements with regions less impacted by U.S. tariffs, China can enhance its ability to maintain growth amid external pressures. This shift not only intends to buffer against tariff-related setbacks but also positions China to become a more dominant player within the global supply chain, capitalizing on the vulnerabilities exposed by a potential U.S. trade war.
Long-term Implications of a Trade War on U.S. Economy
The long-term implications of a trade war with China may significantly reshape the U.S. economy, potentially leading to prolonged instability. Economists warn that steep tariffs might initiate a cycle of retaliatory measures, with other trading partners also implementing restrictions that could escalate tensions across markets. This outcome could stifle growth and innovation in the U.S. as companies become hesitant to invest in new opportunities, crippled by the pervasive uncertainty that comes with changing trade dynamics.
Additionally, the trade policies may alienate U.S. allies, as they too might feel the economic pinch from U.S. tariffs. This erosion of trust could lead to reduced cooperation on broader global issues like climate change or military alliances, posing long-lasting damage to international relations. The prevailing view among economists is that a calculated approach to tariffs that avoids aggressive measures would better serve the long-term economic health of the U.S., fostering both domestic growth and strong international relations.
The Role of Allies in Navigating Tariff Challenges
In the context of an evolving economic landscape marked by rising tariffs, the role of U.S. allies becomes increasingly crucial. Collaborative efforts among countries facing similar economic pressures can lead to innovative approaches towards trade and tariffs. By aligning with partners who share concerns over rising protectionist policies, the U.S. could forge formidable alliances, enhancing collective bargaining power while navigating the complexities of global trade dynamics. Such collaboration can deter unilateralism and promote a more stable economic environment.
Furthermore, U.S. interactions with its allies under the pressure of tariffs could yield opportunities for deeper economic integration. Joint initiatives involving trade agreements can counter challenges posed by tariffs and bolster market resilience. U.S manufacturing, therefore, needs to pivot and consider a more partnership-oriented approach that leverages the benefits of collaboration over isolation. This could prove essential for ensuring that maintaining close ties with allies not only helps weather the adverse effects of tariffs but also propels joint economic advancements.
Potential Shifts in Consumer Behavior Due to Tariffs
In light of imposing tariffs, a notable shift in consumer behavior is likely to arise as Americans adjust to new market realities. Faced with increased prices due to levies on imports, consumers may begin to reconsider their purchasing patterns, favoring domestic products over foreign ones. This pivot could incentivize local manufacturers to ramp up production, potentially leading to a revitalization of certain sectors within the U.S. economy. However, this market shift will only occur if the quality and affordability of domestic alternatives meet consumer expectations.
Simultaneously, as consumers become increasingly conscious of how tariffs influence prices, a trend toward minimalism and value-based purchasing may develop. Buyers may prioritize essential goods, favoring brands that provide greater transparency about their sourcing and manufacturing practices. The awareness around spending could lead to a more informed consumer base, which, in the long run, might shape the competitive landscape as companies adapt to meet this new demand for ethics and sustainability.
The Political Dimensions of Tariff Policies
Tariff policies are not merely economic instruments; they also carry significant political weight. The political motivations behind imposing tariffs often intertwine with national security, labor market protection, and broader foreign relations strategies. Policymakers may use tariffs as a tool to appease domestic audiences yearning for protection against foreign competition, while also promoting a narrative of reinforcing national interests. As seen with past administrations, the implementation of tariffs can often serve as a rallying point for political agendas aimed at preserving jobs and industries vulnerable to foreign competition.
Moreover, the political scene surrounding tariff implementation can escalate into larger geopolitical tensions, as nations respond to perceived threats with corresponding measures. The result may create a volatile environment where trade becomes a pawn in broader diplomatic maneuvering, affecting everything from international relations to defense strategies. Understanding these political dynamics is essential for businesses and consumers alike, as the interplay between trade and politics becomes increasingly pronounced and complex.
Preparing for the Future: Strategic Responses to Trade Challenges
As companies, consumers, and policymakers face the evolving landscape of trade and tariffs, strategic planning is vital for ensuring resilience in the face of uncertainty. Organizations are encouraged to reevaluate supply chain strategies, consider diversification of suppliers, and explore domestic production as viable alternatives. Developing responsive strategies that can adapt to sudden policy changes will be crucial for mitigating potential disruptions and maintaining competitiveness in a challenging market environment.
On the consumer side, awareness and adaptability will be essential as individuals navigate an ever-changing marketplace influenced by tariffs. Understanding the implications of trade policies on price and availability will empower consumers to make informed choices. As both the marketplace and consumer expectations evolve, fostering a culture of strategic thinking and planning will support sustainable growth and adaptability in the face of unanticipated challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of tariffs on the US economy in relation to China?
The impact of tariffs on the US economy, particularly regarding China, could be quite significant. Imposing high tariffs on Chinese imports may lead to increased prices for American consumers, disrupt the global supply chain, and potentially result in a recession. While tariffs are intended to protect domestic industries, they can raise costs for consumers and businesses that rely on imported goods, thereby slowing economic growth.
How do China tariffs impact US-China trade relations?
China tariffs negatively influence US-China trade relations by fostering hostility and uncertainty between the two nations. When tariffs are imposed, it often leads to retaliatory actions, escalating tensions and creating a cycle of trade conflicts. These disputes can undermine longstanding trade partnerships and discourage foreign investments, further complicating diplomatic relations.
What are the tariff implications for consumers regarding China imports?
The tariff implications for consumers related to imports from China include higher prices for everyday goods, as manufacturers often pass along the costs of tariffs. Goods such as electronics, clothing, and household items may see significant price increases, which can strain household budgets and diminish purchasing power in the US market.
How might China’s economic strategy adapt to the challenges posed by US tariffs?
In response to US tariffs, China’s economic strategy may shift towards increasing domestic consumption and seeking new markets to mitigate losses. This includes enhancing the Belt and Road Initiative and fostering trade with other nations. Additionally, China may diversify its supply chains and invest more in emerging economies to counterbalance the negative impacts of decreased exports to the US.
What are the potential global supply chain disruptions caused by China tariffs?
The potential global supply chain disruptions due to China tariffs include delays in production and shipping, increased costs for businesses, and an overall reduction in supply chain efficiency. As companies seek to circumvent tariffs, they may face challenges in sourcing materials and components, leading to a ripple effect that affects various countries and industries globally.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Impact of Tariffs on U.S. Economy | Potential increase in consumer prices, supply chain disruptions, and labor shortages. |
| Effect on China’s Economy | China’s economy faces challenges, including reduced exports to the U.S. and declining market share. |
| Political and Economic Strategies | China may use tariffs as a negotiation tactic and explore new markets and alliances. |
| Shift in Global Trade Dynamics | Potential for countries like India and Vietnam to fill gaps in U.S. imports, but significant challenges remain. |
| Long-term Consequences | Increased tensions could lead to closer ties between China and U.S. allies, harming U.S. foreign relations. |
Summary
The impact of China tariffs could backfire on the U.S., as economists warn that high tariffs may lead to increased prices for American consumers and strain foreign relations. While intended to weaken China’s economy, these tariffs could inadvertently foster stronger alliances among U.S. adversaries, making it a diplomatic and economic concern for the future.