Income inequality has emerged as a critical issue in contemporary society, prompting urgent discussions around wealth redistribution and the billionaire impact on economic justice. With the world’s richest accumulating unprecedented wealth, the debate over their role in society intensifies, especially in terms of philanthropy and the ethics of their contributions to public welfare. The stark reality is that while billionaires like Bill Gates invest in initiatives aimed at combating poverty and fostering green energy solutions, their extreme wealth can also exacerbate societal divides and environmental degradation. This paradox raises important questions about taxation and equity, and whether the super-rich are ultimately beneficial or detrimental to the broader community. As we explore the intricate dynamics of income inequality, it becomes clear that finding a balance in wealth distribution is vital for creating a fairer and more sustainable future.
The growing disparity between rich and poor, often referred to as economic inequality, has spurred a multifaceted debate about the moral implications of concentrated wealth. Some argue for a re-evaluation of our approach to wealth distribution, highlighting the need for equitable taxation methods that can redistribute resources effectively. The discussion extends beyond mere numbers; it probes the philosophical considerations of fairness and justice, questioning whether current systems truly reflect a meritocratic society. With terms such as wealth disparity and social equity frequently entering the conversation, it is crucial to examine how these concepts intersect with policies affecting those at the economic margins. As we delve into alternatives for tackling this pressing issue, the conversation must include not just the potential of philanthropy but also a comprehensive review of market dynamics that influence the livelihoods of countless individuals.
The Ethics of Wealth Redistribution
Wealth redistribution remains a contentious topic within modern economic discourse, eliciting strong arguments from both sides. Advocates for redistribution argue that the stark contrast between the super-rich and the impoverished creates social and economic injustices, exacerbating issues like poverty, environment degradation, and inequality. Philosophers and economists alike suggest that reallocating resources from those who hold them excessively, namely billionaires, to those in need represents not only a moral imperative but a pathway toward greater economic justice. This approach challenges the prevailing notion that accumulated wealth solely equates to merit, emphasizing instead that structural changes could lead to a more equitable society.
Opponents of wealth redistribution, however, caution against the negative ramifications it might impose on economic incentives and innovation. They argue that billionaires often drive forward technological advances and job creation, providing services and opportunities that can uplift entire communities. The philanthropy debate, particularly when addressing billionaires’ contributions to social causes, raises questions about their genuine intentions versus their quest to alleviate the consequences of systemic wealth inequality. Hence, a balance must be sought between supporting economic growth and addressing the pressing need for more equal societal structures.
Understanding Income Inequality
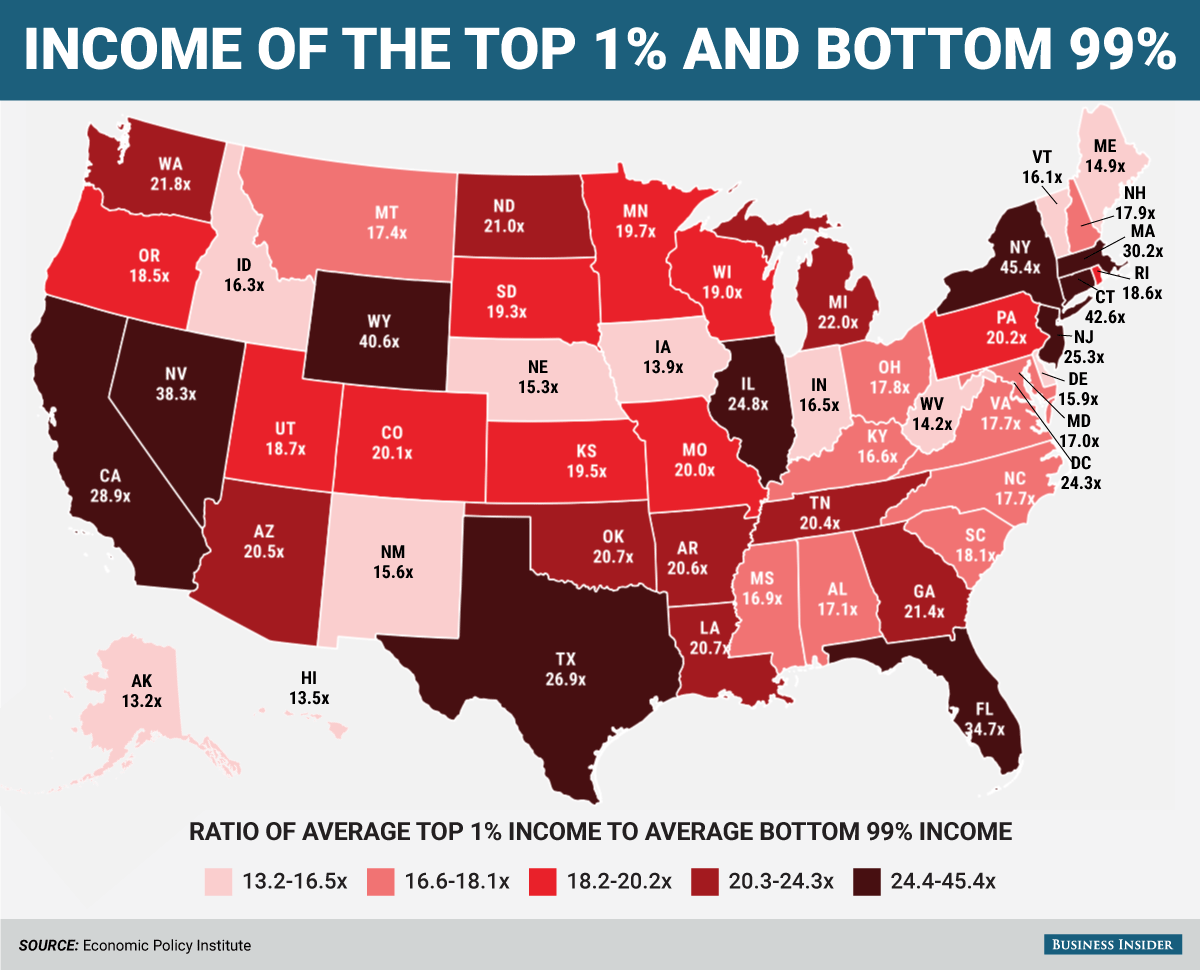
Income inequality, defined as the uneven distribution of income across various participants in an economy, has drawn significant attention from economists and policymakers. The recent debate surrounding the rising income differences has illuminated the fundamental disparities that exist not only in salaries but also in access to resources and opportunities. The statistics are stark; a substantial portion of global wealth is controlled by a mere fraction of the population, which stifles social mobility and reinforces cycles of poverty. This phenomenon leads to calls for economic justice and redistributive policies that can mitigate the adverse effects of wealth concentration.
Moreover, income inequality can have grave implications for societal cohesion and democratic processes. When wealth becomes concentrated among a few, it can lead to corruption, where policymakers prioritize the interests of the affluent over the majority’s needs. Discussions around taxation and equity are increasingly centered on how to rectify these imbalances. Proposals range from progressive taxation systems that require higher contributions from the wealthy to wealth taxes that target extensive holdings, aiming to ensure that everyone has access to essential services and opportunities, thereby fostering a fairer society.
The Billionaire Impact on Society
Billionaires have been both celebrated for their contributions to philanthropy and criticized for their role in perpetuating socioeconomic disparities. Their immense wealth offers them the ability to influence public policy and societal outcomes profoundly. Some billionaires, like Bill Gates, have committed substantial resources to combat global issues such as poverty and disease, positioning themselves as agents of positive change. This impact, however, is viewed with skepticism by some who argue that their influence can lead to a distortion of democratic norms and public interests. Critics contend that reliance on the philanthropic pursuits of billionaires may detract from the responsibility of government to ensure social welfare.
Furthermore, the issue of billionaires’ environmental impact cannot be overlooked. Their consumption patterns often contribute to significant carbon emissions, positioning them as central figures in the discourse on environmental justice. The juxtaposition of their contributions through green initiatives against their environmental footprint sparks vital debates about the priorities of wealth holders. A more equitable approach could involve empowering ordinary citizens to have a stake in ecological decision-making, ensuring that environmental policies reflect the broader population’s interests rather than catering solely to wealthy individuals.
The Philanthropy Debate: Altruism or Self-Interest?
Philanthropy appears to offer a constructive avenue for billionaires to address pressing social issues; however, it raises critical questions about the intentions behind such generosity. The philanthropy debate revolves around whether these acts are genuinely altruistic or if they serve to mitigate negative public perceptions of wealth accumulation. Investors like Elon Musk and Jeff Bezos have been lauded for their charitable endeavors, yet skeptics argue that their contributions may merely put a Band-Aid on systemic issues rather than advocate for structural reforms that could promote economic justice and equity.
Moreover, this debate also touches upon the power dynamics at play when billionaires take on philanthropic roles. As they allocate funds to various causes, they wield significant influence over which issues receive attention and resources. This concentration of power can lead to a landscape where foundational societal needs are overlooked in favor of projects that align more closely with their interests. The challenge lies in ensuring that philanthropy complements government efforts rather than replaces them, advocating for systemic change that prioritizes equitable wealth distribution and community empowerment.
Taxation and Equity: A Balanced Approach
Taxation is often hailed as a tool for fostering equity within an economy, particularly in addressing income inequality. Proponents of higher taxes on the wealthy assert that doing so can help finance social programs and infrastructure that benefit the broader population. Progressive taxation is seen as a justifiable means to redistribute wealth from those who have disproportionately benefitted from the economic system, toward communities in need. Yet, the actual taxation structure often reveals glaring loopholes that enable wealthy individuals to evade their fair share of tax obligations, thereby exacerbating inequality.
On the other hand, any proposal for increased taxation must navigate the fears of disincentivizing investment and entrepreneurship. Critics argue that excessive taxation could stifle economic growth, discouraging the type of wealth creation that can lead to job opportunities and improved living standards. Thus, the challenge remains in constructing a tax system that achieves equity without impeding the market’s capacity to thrive. Dialogue must focus on identifying efficient tax policies that balance these concerns, paving the way for a fairer and more prosperous society.
Exploring Economic Justice in a Wealthy Society
Economic justice is an ideal where all individuals have fair access to resources and opportunities, irrespective of their socio-economic background. A critical examination reveals that the current economic systems often fail to uphold this ideal, leaving vast populations marginalized. The discussions held during the ethics debate underscore the urgency of creating frameworks that not only promote wealth creation but also facilitate equitable distribution of resources. As we grapple with income disparity, the call for economic justice advocates for policies that hold the powerful accountable while empowering the less fortunate.
Moreover, the notion of economic justice invites a critical assessment of the structures that perpetuate inequality. Addressing unjust economic practices requires collaboration from various sectors, including government, business, and civil society. Innovative solutions such as property-owning democracy can offer alternatives that enable broader wealth distribution while fostering individual entrepreneurship. By tackling the root causes of economic inequality and advocating for systemic reform, we can move closer to realizing a society that truly embodies the principles of economic justice.
Corporate Responsibility and the Global Economy
In today’s interconnected global economy, the responsibility of corporations extends beyond profit-making to encompass their societal and environmental impact. Large corporations, particularly those like Walmart, face scrutiny over their labor practices and the effects they have on local economies. Advocates argue that businesses should take an ethical approach to corporate responsibility, ensuring fair wages and working conditions that support their employees and the communities they serve. The intersection of corporate strategy and social responsibility becomes increasingly critical as consumers demand accountability from the brands they support.
Additionally, corporations need to adopt sustainable practices that consider their environmental footprint. The reliance on cheap labor and materials often leads to practices that are detrimental to both social equity and environmental sustainability. Businesses are called to rethink their operational models and contribute positively to the communities they engage with. By prioritizing corporate social responsibility, companies can play a pivotal role in reducing income inequality while also committing to sustainable practices that protect the environment for future generations.
The Role of Education in Addressing Inequality
Education stands as a pivotal factor in breaking the cycle of poverty and reducing income inequality. Access to quality education equips individuals with the skills and knowledge necessary to improve their economic circumstances. Yet, disparities in educational opportunities often mirror societal wealth gaps, where low-income communities struggle to provide adequate resources for their youth. The conversations surrounding education must address how to create equitable systems that ensure all children, regardless of their background, receive access to high-quality education, thus enabling upward mobility.
Moreover, educational reform must also focus on inclusivity and representation. Discussions in the ethics debate highlighted that it is not just about financial investment in education but also about fostering environments where diverse perspectives are embraced. By encouraging diverse voices in educational settings, we can better prepare future generations to navigate an increasingly complex world while promoting understanding and collaboration across different socio-economic backgrounds. The investment in education necessities a long-term commitment from both public and private sectors, leading to a more equitable future.
Innovative Solutions to Combat Wealth Disparity
Innovative approaches are essential in addressing the rising tide of wealth disparity. Traditional economic models may no longer suffice in creating frameworks that work for everyone. Strategies such as technology-driven businesses and cooperative models offer solutions that empower individuals by distributing ownership and profits more equitably within communities. Through democratizing wealth ownership, individuals can have a stake in their economic well-being, which can significantly reduce income inequality in a sustainable manner.
Additionally, advancements in technology can provide opportunities for new job creation and economic participation, particularly for underserved populations. Initiatives that embrace technological innovations promise to enhance access to resources and information, hence fostering a more inclusive economy. By harnessing tech’s ability to bridge gaps, we can create environments conducive to economic justice, where prosperity is shared equitably, leading to sustainable growth for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is income inequality and how does it affect society?
Income inequality refers to the unequal distribution of income within a population, often measured by the income gap between the richest and poorest individuals. This disparity can lead to social unrest, limit economic mobility, and create barriers to accessing essential services like healthcare and education. Addressing income inequality is crucial for promoting economic justice and ensuring a fairer society.
How does wealth redistribution impact income inequality?
Wealth redistribution involves reallocating resources from the wealthy to the disadvantaged, often through taxation and social programs. This process can significantly reduce income inequality by providing low-income individuals with better access to resources, opportunities, and services. Effective wealth redistribution promotes economic equity and aids in creating a more balanced society.
What role do billionaires play in income inequality?
Billionaires can exacerbate income inequality by accumulating vast resources that dominate economic power. Some argue that their contributions to philanthropy and job creation provide societal benefits. However, critics highlight that the immense wealth of billionaires can also lead to environmental harm and social stratification, making their overall impact on income inequality a debated issue.
Is there a debate surrounding philanthropy and income inequality?
Yes, the philanthropy debate centers on whether billionaire philanthropy effectively addresses income inequality or merely offers a band-aid solution. Proponents argue that charitable contributions from the wealthy can direct funds to vital social issues, while critics contend that these efforts distract from systemic changes needed to achieve true economic justice and equity.
How does taxation affect economic equity and income inequality?
Taxation plays a critical role in promoting economic equity by redistributing wealth from higher income brackets to fund public services and social safety nets. Progressive taxation systems aim to reduce income inequality by imposing higher tax rates on the wealthy, facilitating investments in education, healthcare, and other services that benefit lower-income populations.
What are the potential solutions to reduce income inequality?
Solutions to reduce income inequality include implementing progressive taxation, enhancing workers’ rights, promoting unionization, investing in public services, and creating policies that encourage equitable wealth distribution. Embracing models like property-owning democracy or democratic socialism may also provide frameworks for addressing systemic inequalities.
How does foreign immigration relate to income inequality in wealthy countries?
Foreign immigration can significantly impact income inequality by providing labor and contributing to economic growth. Allowing immigrants into wealthy countries can address workforce shortages and promote innovation. However, challenges remain in ensuring that the benefits of this immigration are equitably shared, rather than exacerbating existing income inequality.
| Key Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Impact of Billionaires | Billionaires invest in social initiatives but also contribute to environmental harm. |
| Redistribution of Wealth | Some argue that getting rid of billionaires and redistributing wealth could benefit society, particularly in green technologies. |
| Market Dynamics | Market incentives can lead billionaires to create jobs and enhance infrastructure, benefiting the poor. |
| Role of Luck in Wealth | Wealth creation is often arbitrary and influenced by factors outside individual control, challenging meritocracy. |
| Corporate Practices | Companies like Walmart provide affordable goods but exploit workers and can harm local economies. |
| Alternative Economic Systems | Exploring democratic socialism and cooperative business models to create fairer labor practices. |
| Norwegian Model | A strong economy like Sweden’s demonstrates that billionaires can coexist with effective public institutions to benefit all. |
| Addressing Inequality | Expanding immigration policies might be one effective method to improve the lives of the poorest globally. |
Summary
Income inequality continues to be a predominant issue in society today, as illustrated in the recent panel discussion hosted by the Edmond and Lily Safra Center for Ethics. The debate featured various perspectives on the role of billionaires in our economy, the ethics of wealth redistribution, and the implications on social justice. Panelists presented compelling arguments both for and against the presence of extreme wealth, suggesting that while billionaires may contribute positively through philanthropy and job creation, their impact can also exacerbate environmental issues and social inequalities. As the global wealth gap widens, the conversation around income inequality must evolve to include innovative solutions like property-owning democracy and reforming corporate practices to ensure a fair economic landscape for all.